
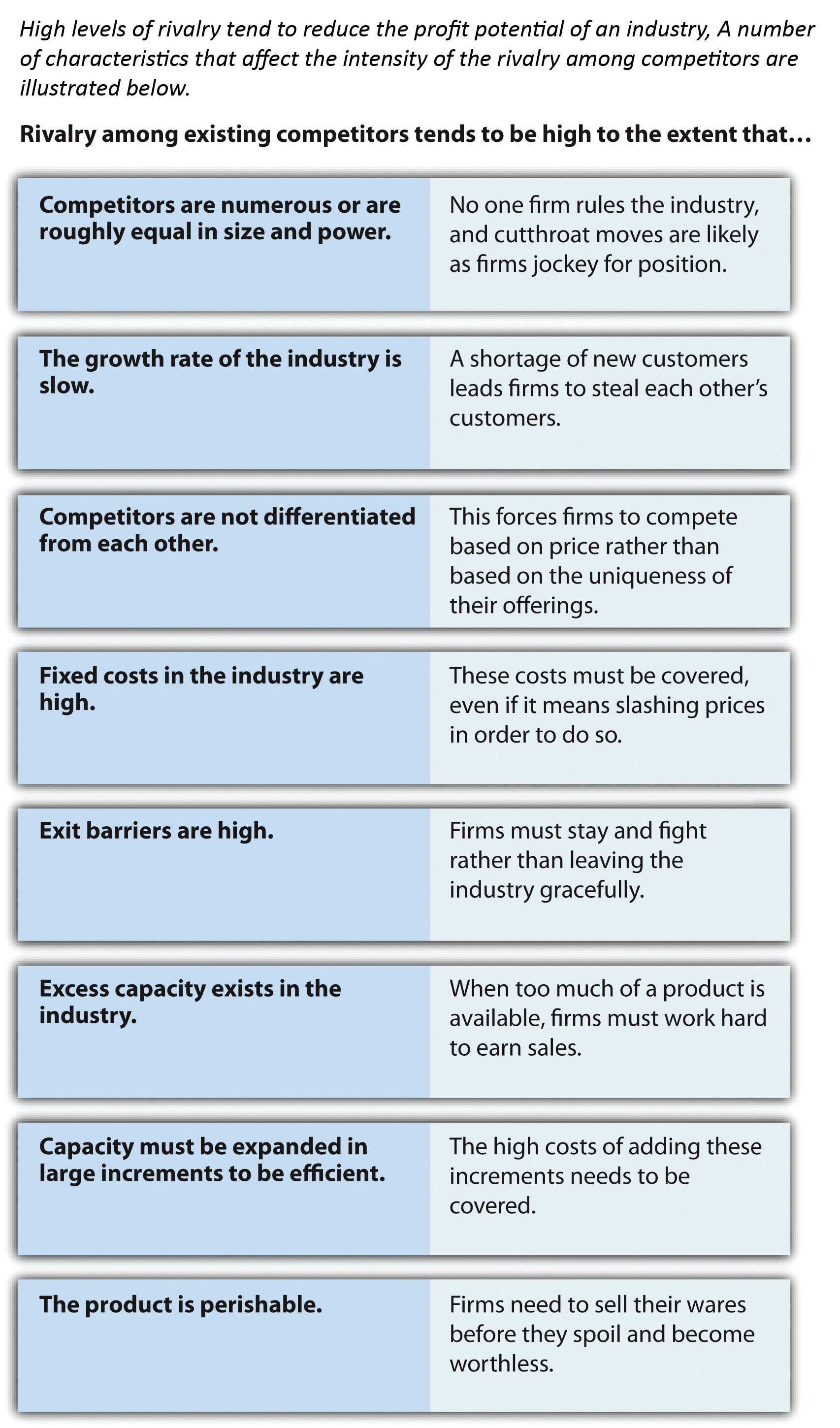
Rivalry tends to be fierce, for example, to the extent that the growth rate of demand for the industry’s offerings is low (because a lack of new customers forces firms to compete more for existing customers), fixed costs in the industry are high (because firms will fight to have enough customers to cover these costs), competitors are not differentiated from one another (because this forces firms to compete based on price rather than based on the uniqueness of their offerings), and exit barriers Factors that make it difficult for a firm to stop competing in an industry. If, on the other hand, competitors avoid bitter rivalry, then price wars can be avoided and profit potential increases.Įvery industry is unique to some degree, but there are some general characteristics that help to predict the likelihood that fierce rivalry will erupt. When competition is bitter and cutthroat, the prices competitors charge-and their profit margins-tend to go down. Of particular concern is whether firms in an industry compete based on price. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among an industry’s competitors is important because the degree of intensity helps shape the industry’s profit potential. Former CEO Ray Kroc allegedly once claimed that “if any of my competitors were drowning, I’d stick a hose in their mouth.” While this sentiment was (hopefully) just a figure of speech, the announcement in March 2011 that Subway had surpassed McDonald’s in terms of numbers of stores might lead the hostility of McDonald’s toward its rival to rise. This is illustrated by a quote from the man who built McDonald’s into a worldwide icon. Subway faces fierce competition within the restaurant business, for example. Because competitors seek to serve the same general set of buyers, rivalry can become intense ( Figure 3.9 "Rivalry"). Competitors use a variety of moves such as advertising, new offerings, and price cuts to try to outmaneuver one another to retain existing buyers and to attract new ones. in an industry are firms that produce similar products or services. The competitors The set of firms that produce goods or services within an industry.
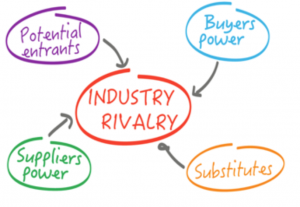
The Rivalry among Competitors in an Industry If the situation looks bleak, for example, one possible move is to exit the industry. Once executives determine how much profit potential exists in an industry, they can then decide what strategic moves to make to be successful. This could involve, for example, all five forces providing firms with modest help or two forces encouraging profits while the other three undermine profits. Most industries lie somewhere in between these extremes. If all the forces work to undermine profits, then the profit potential is very weak.

If none of these five forces works to undermine profits in the industry, then the profit potential is very strong. To do so, five forces analysis considers the interactions among the competitors in an industry, potential new entrants to the industry, substitutes for the industry’s offerings, suppliers to the industry, and the industry’s buyers. The purpose of five forces analysis is to identify how much profit potential exists in an industry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
